
Early assessment and in‐hospital management of patients with acute myocardial infarction at increased risk for adverse outcomes: a nationwide perspective of current clinical practice. 1996 27:1119-1127īecker RC, Burns M, Gore JM, Spencer FA, Ball SP, French W, Lambrew C, Bowlby L, Hilbe J, Rogers WJ. Myocardial infarction patients in the 1990s-their risk factors, stratification and survival in Canada: the Canadian Assessment of Myocardial Infarction (CAMI) Study. Rouleau JL, Talajic M, Sussex B, Potvin L, Warnica W, Davies RF, Gardner M, Stewart D, Plante S, Dupuis R, Lauzon C, Ferguson J, Mikes E, Balnozan V, Savard P. By incorporating events during the index hospitalization, it can better define risk and help to guide treatment decisions. This score is a prospectively derived, validated means of estimating 1-year mortality of STEMI at hospital discharge and can serve as a clinically useful tool. In the validation database, the C-statistic was 0.81, with a NRI of 0.35 (P=0.01). The C-statistic produced by the dynamic score in the derivation database was 0.76, with a net reclassification improvement (NRI) of 0.33 (P<0.0001) from the inclusion of dynamic events to the original TIMI risk score.
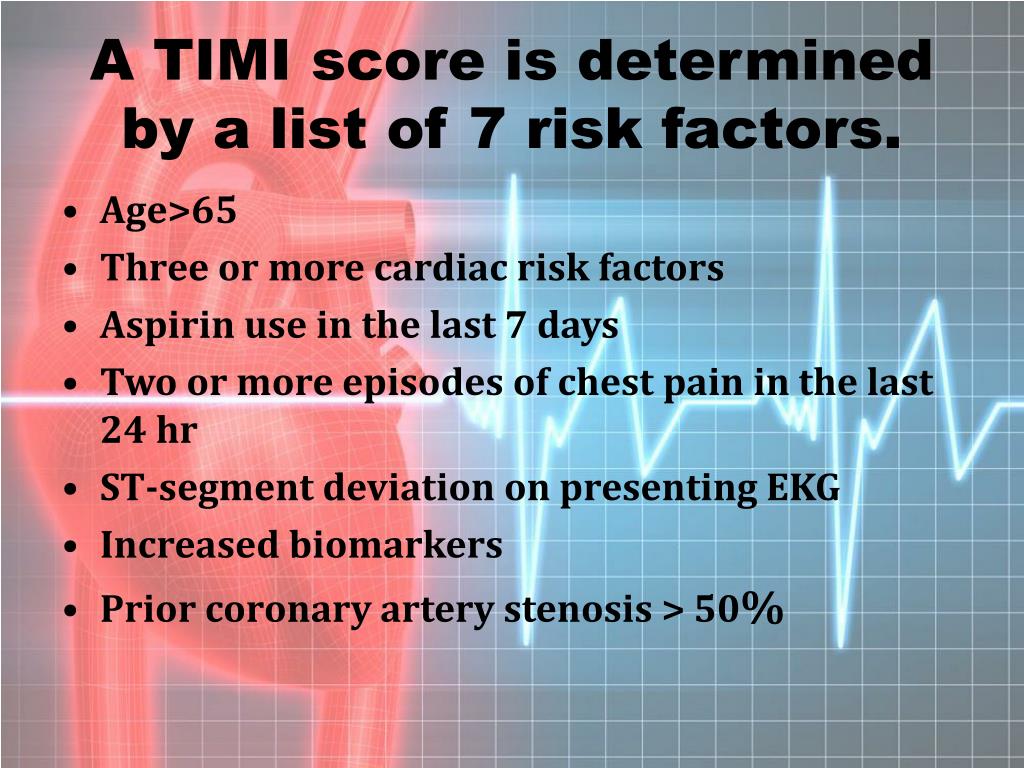
The dynamic score included the development of in-hospital MI, arrhythmia, major bleed, stroke, congestive heart failure, recurrent ischemia, and renal failure. Each variable was assigned an integer value based on the odds ratio, and the final score was the sum of these values.
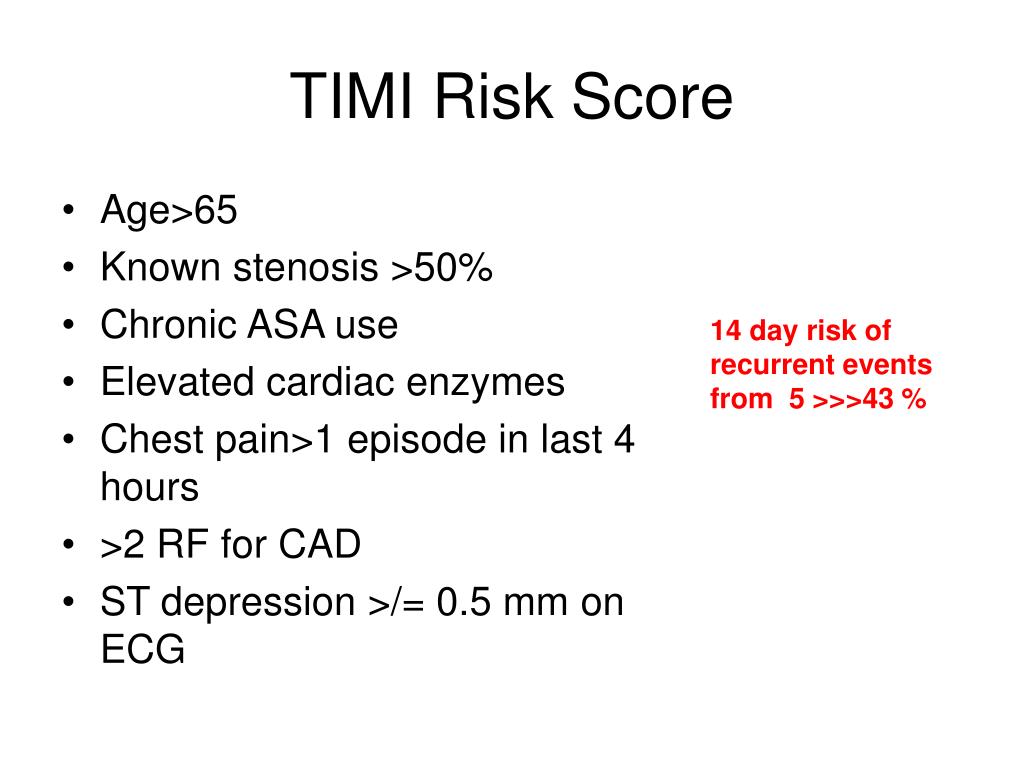
#Variables of timi risk score full#
Variables with P<0.05 were incorporated into a full multivariable Cox model to assess the risk of death at 1 year. Each variable was tested individually in a univariate Cox proportional hazards regression. New variables were major clinical events occurring during the index hospitalization. Baseline variables were from the original TIMI risk score for STEMI. The dynamic TIMI risk score for STEMI was derived in ExTRACT-TIMI 25 and validated in TRITON-TIMI 38.

A dynamic risk score provides an initial risk stratification and reassessment at discharge. Compared to other biomarkers, NT-proBNP is the strongest independent predictor of in-hospital and 180-day mortality.Although there are multiple methods of risk stratification for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), this study presents a prospectively validated method for reclassification of patients based on in-hospital events. In NSTE-ACS, NT-proBNP adds substantial information to the TIMI risk score and the ACC/AHA classification. NT-proBNP was not an independent predictor of risk of new myocardial infarction, even in the acute or long term. 001), and added significant prognostic information to the TIMI and ACC/AHA prognostic categories. Adjusting by clinical, ECG variables, and biomarkers, NT-proBNP concentration was the strongest independent predictor of in-hospital (OR 1.7, 95% CI: 1.31-2.20, p <. We prospectively studied the additive value of N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in relation to the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score and the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) joint prognostic classification, and compared the predictive capacity of NT-proBNP, troponin T (TnT), C-reactive protein (hsCRP), myoglobin, and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) concentrations in a cohort of 1483 consecutive patients with non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE-ACS).Ĭentralised measurements of NT-proBNP, TnT, myoglobin, and hsCRP were performed 3 h (median) after admission.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
